| Evaporation and spread of surfactant amended droplets on leaves |

|
|
In order for pesticide applications to be effective,they need to cover the treated area uniformly with a desired dose.The area of coverage is determined in part by the process of evaporation and spread ofthe droplets on a leaf surface. This process varies with the type of leaf surface (hairy vs. waxy, for example) and the physical properties of the pesticide. Nonionic surfactants are often recommended for use in formulations and tank mixtures to increase the effectiveness of foliar-applied pesticide spray treatments. Nonionic surfactants break the surface tension so pesticide droplets spread more evenly and adhere longer on leaf surfaces. Spray mixtures containing surfactants can provide better spray coverage, longer-lasting residue, better active ingredients uptake, and improved penetration of the active ingredient into leaf tissue.This can result in better efficacy, less pesticide use, and less overall cost. Close-up videos (below) recorded in Dr. Heping Zhu's lab clearly demonstrate the differences in the spread and evaporation process of a single droplet with and without surfactant on hairy and waxy leaf surfaces. |
|
|
|
|
|
There are disadvantages to using surfactants, however, as over use of surfactant can cause an adverse effect on plants. When used in excess, surfactants can enhance the potential for crop injury (phytotoxicity) on the desirable plants. While the addition of nonionic surfactants to pesticide mixtures can increase pesticide efficiency and reduce the corresponding cost of pesticide use, to achieve optimum performance and lessen the potential for unwanted phytotoxicity, always read and follow the label instructions on surfactant selection and use. |
|
The files below demonstrate how droplets spread and evaporate on hairy and waxy leaf surfaces for foliar agro-chemical spray applications with and without surfactants. |
|
Waxy leaf no surfactant top view |
For more information see: Evaporation and deposition coverage area of droplets containing insecticides and spray additives on hydrophilic, hydrophobic and crabapple leaf surfaces. Dispersion and evaporation of droplets amended with adjuvants on soybeans. Characterization of dynamic droplet impaction and deposition formation on leaf surfaces. Dynamics of water droplet impact and spread on soybean leaves. Determination of foliar uptake of water droplets on waxy leaves in controlled environmental system. Coverage Area and Fading Time of Surfactant-Amended Herbicidal Droplets on Cucurbitaceous Leaves. Amendment of Herbicide Spray Solutions with Adjuvants to Modify Droplet Fading Activities on Weeds. 3D optical surface profiler for quantifying leaf surface roughness. Impact and Adhesion of Surfactant-Amended Water Droplets on Leaf Surfaces Related to Roughness.
|
| ARS contact: Heping Zhu |

 Droplets containing a surfactant deposited on a waxy geranium leaf surface have a much larger area of coverage than droplets without the surfactant.
Droplets containing a surfactant deposited on a waxy geranium leaf surface have a much larger area of coverage than droplets without the surfactant.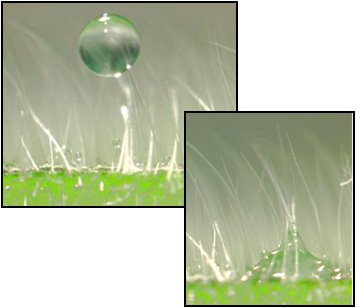 Similarly, on a hairy geranium leaf surface, droplets containing a surfactant penetrate and spread along paths between hairs while the same size droplet without the surfactant remains on top of the hairs and does not readily spread out.
Similarly, on a hairy geranium leaf surface, droplets containing a surfactant penetrate and spread along paths between hairs while the same size droplet without the surfactant remains on top of the hairs and does not readily spread out.