In 2019, the federal government allocated $68.9 million to build a new GGRU facility in Geneva. The funding will create a new lab for USDA Agricultural Research Service scientists. Dr. Zhong says the new yet unnamed facility is expected to open in three years. Cornell will be involved as a partner in the facility and research once the lab is built (Gan-Yuan Zhong).
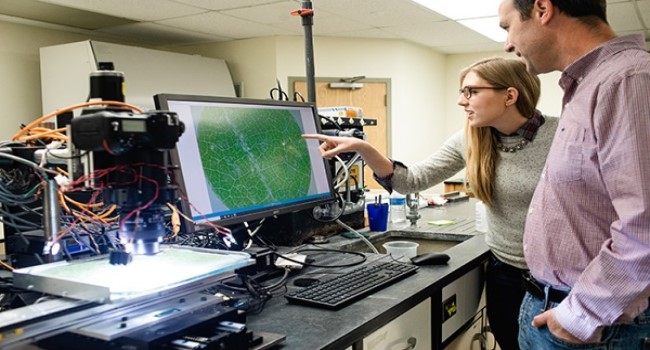
USDA-ARS scientists Anna Underhill and Lance Cadle-Davidson analyze powdery mildew resistance using data from an imaging robot (Cadle-Davidson, Lance).
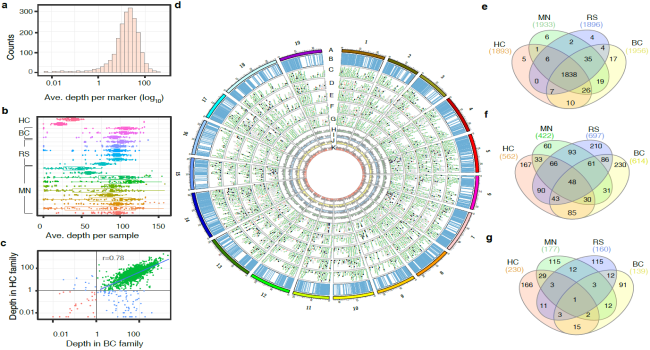
This figure describes our 2000 core genome markers that work across grapes and muscadines (Cadle-Davidson, Lance).
(*Click on photo to view paper).*Goes to Non-Federal Site
USDA cold hardy grapevine germplasm during winter conditions (Londo, Jason).
Variation in grapevine plant architecture caused by modifications of genes controlling plant height.
Wild grapevine (V. rupestris) is often used for rootstocks for cultivated grapes (Londo, Jason).
Young wild grape inflorescence in spring (Londo, Jason).
Grafting grapevine. Marquette scion, experimental rootstock (Londo, Jason).
Phylloxera infected leaves (Londo, Jason).
One million powdery mildew spores are produced each day on a single leaf of a susceptible grapevine (Cadle-Davidson, Lance).
Powdery mildew spore under a microscope, visualized with fluorescent stain (Cadle-Davidson, Lance).
By sampling a small 1-cm leaf disc for each grapevine, the disease resistance of over 300 grapevines (from a half-acre vineyard) can be tested in a small environment like a baking dish (Cadle-Davidson, Lance).
Assessing powdery mildew resistance in grapevine (Cadle-Davidson, Lance).
Phone: 315-614-9665
630 West North Street
Geneva, NY 14456