| Use of Hsp90 for nematode phylogeny and identification |

|
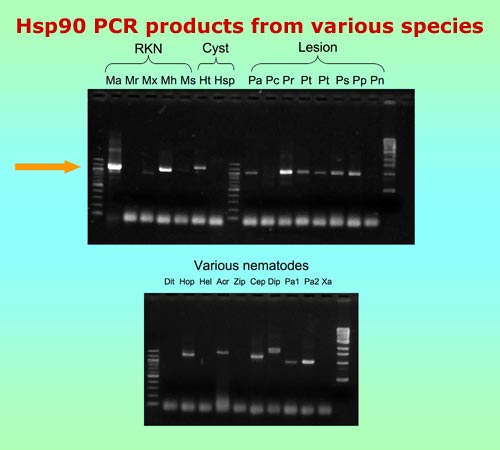
We originally became interested in the gene encoding the heat shock protein Hsp90 when studying genes involved in developmental arrest in the free-living nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Due to its relatively conserved sequence, Hsp90 has also been used as a phylogenetic marker in a wide range of organisms. Since there is great need for additional genes for strengthening nematode phylogeny, we sought to determine the usefulness of Hsp90 for this purpose.
Over the past several years, it has become apparent that C. elegans codon usage differs substantially from that of many plant-parasitic nematodes. To amplify the Hsp90 gene, we designed new PCR primers and cycling conditions useful for a wide variety of plant-parasitic nematode species.
PRIMER
U831
U288
L1110BF/R
F
F
R5'-> 3' SEQUENCE
AAYAARACMAAGCCNATYTGGAC
GAYACVGGVATYGGNATGACYAA
TCGCARTTCTCCATRTYTGGAC
PCR fully described in Skantar and Carta, 2005; modified from Skantar and Carta, 2000.
25 ?l reactions:
500?M each primer
200?M dNTPs
1 unit Taq polymerase
1x Taq buffer
template ~20 ng genomic DNA or 1?l "nematode smash" extract
| 1 cycle:o 45 cycleso o o o 1 cycle:o | 94oC 2 min 94oC 20s 65oC 5s 60oC 5s 55oC 5s 68oC 1 min 65oC 15 min |
Skantar, A. M. and Carta, L. K. Multiple displacement amplification (MDA) of total genomic DNA from Meloidogyne spp. and comparison to crude DNA extracts in PCR of ITS1, 28S D2-D3 rDNA and Hsp90. Nematology 7 (2): 285-293. 2005.