Research Leader
Philipp Simon: Carrot and Garlic Genetics
- Contact me at philipp.simon@usda.gov
- My University of Wisconsin Horticulture Department page
- Vegetable Crops Research Unit home page
- ( A user-friendly URL for this page is https://vcru.wisc.edu/simon/ or https://ars.usda.gov/mwa/msn/simon )
Information
Carrot Trial ResultsOriginal Germplasm Release NoticesGermplasm Resources
Initiative for Future Agriculture and Food Systems (IFAFS) ProjectSpecialty Crops Research InitiativeOrganic Agriculture Research and Extension Initiative - "Carrot Improvement for Organic Agriculture" |
Publications and Scientific Papers
Articles On-Line
Various Interesting Web Sites |
Carrot Pictures
 |
They don't have to be orange, carrots can come in a wide variety of colors derived from several different pigments. |
 |
Root color genes-- P 1, Y, L. |
 |
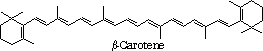
'A Plus'New darker-orange varieties of carrots have been produced by the breeding program. This picture shows one USDA Carrot Variety, 'A Plus', which is high in carotene levels. |
 |
High carotene carrots Left: Beta III, 280 ppm carotene Center: Progenitor, 140 ppm carotene Right: HCM (High Carotene Mass), 500 ppm carotene
|
 |
| Carrot breeding- Small (left) and large (right) isolation cages which are used for controlled crossing of one or more carrot plants. |
 |
Root sugar gene Rs- This single gene in carrot controls the type of sugar in the root.
Sucroseis a disaccharide, composed of one molecule of fructoseattached to one molecule of glucose. Fructose and glucose are reducing sugars, and sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. Thus, the gene name Rsstands for reducing sugar. When this dominant allele (Rs) is present, the carrot root will accumulate the reducing sugars fructoseand glucose. When both recessive alleles (rsrs) are present, the carrot root will accumulate primarily sucrose. These graphs show the distribution of sugar types when a low reducing sugar type rsrs(P1) was crossed with a high reducing sugar type RsRs(P2), producing a hybrid offspring Rsrs(F1). Because Rs is dominant, the F1 resembles P1. A backcross of the F1 with P2 (designated BC1P2) is half RsRsand half Rsrs, both of which are high reducing sugar types. The F1 selfed (F2) should show a 3:1 segregation, due to the distribution of the three possible genotypes 1:RsRs, 2:Rsrs, 1:rsrs.
|
Garlic Pictures
 |
Garlic true seed production- this plant was produced from a true seed of garlic, a rare event, since cultivated garlic has been exclusively propagated vegetatively for many hundreds of years. |
 |
Garlic coat of arms, 1450-1500, Germany |
 |
Garlic, Allium sativum, from the book Hortus Sanitatis, Mainz, 1485. |